Text Extractor
A tool for extracting and repacking text strings from game executable files.
Table of contents
- Overview
- Requirements
- Installation
- Usage
- Technical Details
- File Format
- Error Handling
- Best Practices
- Contributing
- License
Overview
The Text Extractor is a Python script that allows you to:
- Extract text strings from game executable files
- Preserve text offsets for accurate repacking
- Import modified texts back into the executable
- Support UTF-8 encoded text
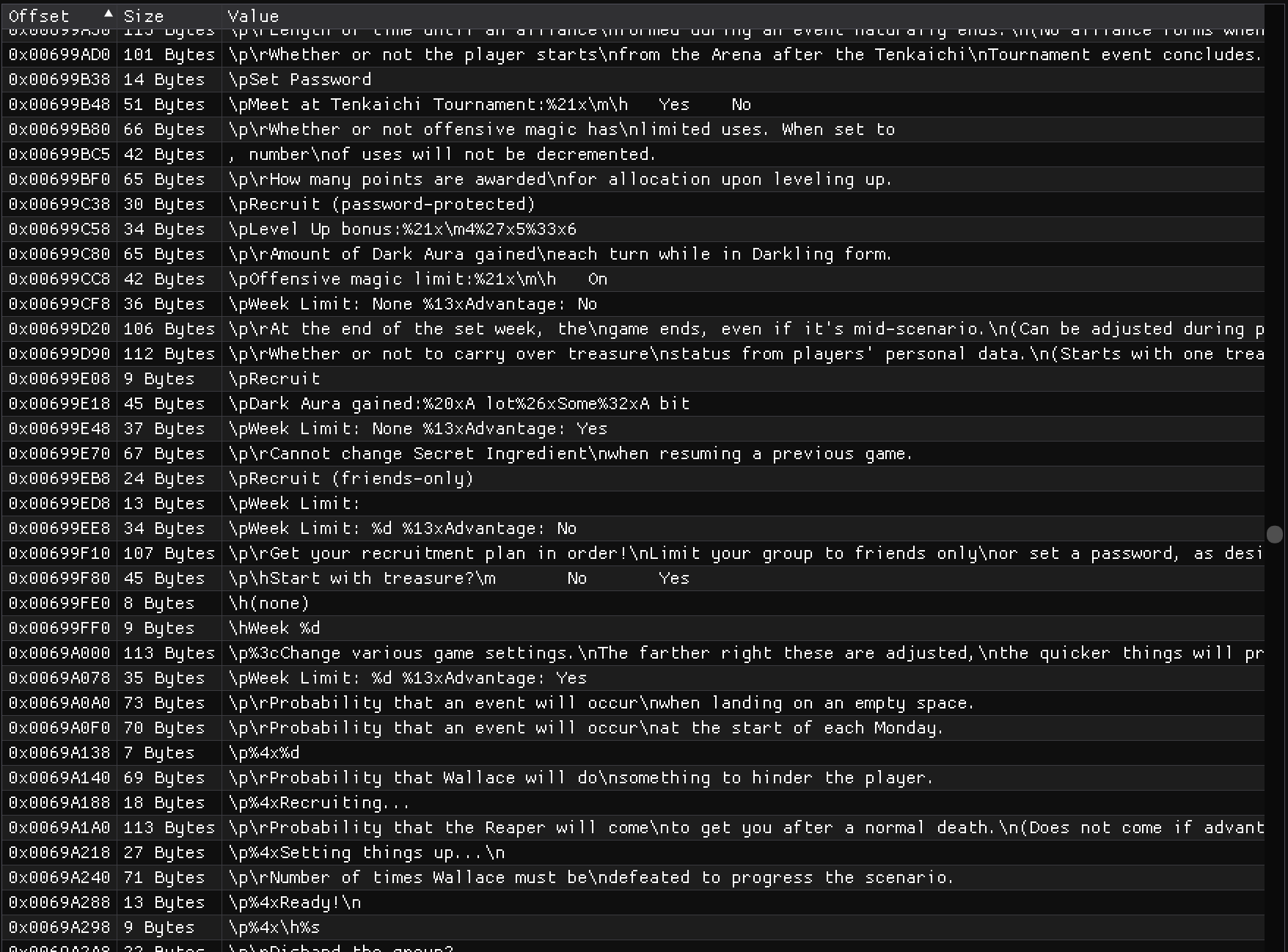
A visual representation of text extraction showing hex values and corresponding text offsets.
Requirements
- Python 3.6 or higher
- Basic knowledge of command line tools
- Text editor for modifying extracted texts
Installation
- Download the
text_extract_repack.pyscript. - Place it in a directory with your target executable file.
Usage
Extracting Text
python text_extract_repack.py extract --exe game.exe --texts output.txt --offsets offsets.txt
This will:
- Scan the executable for text strings
- Save extracted texts to output.txt
- Save text offsets to offsets.txt
Importing Modified Text
python text_extract_repack.py import --exe original.exe --texts modified.txt --offsets offsets.txt --output_exe new_game.exe
This will:
- Read the modified texts and original offsets
- Validate text lengths
- Create a new executable with updated texts
Technical Details
Text Extraction Process
The script uses regular expressions to find text strings:
pattern = rb"\\p.*?(?=\\k|\\z|\x00|\n)"
This pattern matches:
- Strings starting with \p
- Ending at \k, \z, null byte, or newline
- Captures the text content between
Offset Preservation
The script maintains a mapping between texts and their file offsets:
offsets.append(match.start()) # Store original position
This ensures:
- Accurate text replacement
- File structure integrity
- Proper text alignment
UTF-8 Handling
Text processing includes UTF-8 support:
text = match.group(0).decode("utf-8").strip()
Features:
- UTF-8 decoding of extracted text
- Proper handling of special characters
- Error handling for invalid encodings
Import Validation
When importing modified texts:
if len(new_text) > original_length:
print(f"New text too long for offset {offset}. Skipping...")
continue
The script:
- Validates text lengths
- Prevents buffer overflows
- Maintains file integrity
File Format
Extracted Text File
\pExample text 1
\pAnother string
\pGame dialog
Offset File
1234
5678
9012
Each line in the offset file corresponds to the position of the text in the executable.
Error Handling
The script includes comprehensive error checking:
- File Access
try: with open(exe_file_path, "rb") as exe_file: content = exe_file.read() except FileNotFoundError: print("Error: Executable file not found") - Text Decoding
try: text = match.group(0).decode("utf-8").strip() except UnicodeDecodeError: continue - Size Validation
if len(new_text) > original_length: print(f"Warning: Text too long at offset {offset}")
Best Practices
- Backup Files
- Always keep a backup of the original executable
- Save copies of extracted texts
- Text Modification
- Maintain original text length when possible
- Preserve special markers (\p, \k, etc.)
- Use UTF-8 compatible text editors
- Testing
- Test modified executable thoroughly
- Verify text displays correctly
- Check for encoding issues
Contributing
Found a bug or want to improve the tool?
- Report issues on GitHub
- Submit pull requests with improvements
- Share your findings on our Discord
License
This tool is licensed under The Unlicense. You can:
- ✅ Use freely for any purpose
- ✅ Modify and distribute without restrictions
- ✅ No attribution required
- ✅ Dedicated to public domain
- ✅ No warranty provided
See the LICENSE file for full details.
